
Keyless Lock
Most vehicles today have remote controls with two buttons that control the locking and the unlocking of the doors of the vehicles. The development of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology will soon replace this method of opening and closing of the doors. When a transponder is placed near a reader, it will start to communicate with the reader and once the information exchange is successful, the door will open. A transponder consists of an antenna with a microchip which is embedded into a plastic tag. It is usually light weight and is designed to take the impact of normal mechanical stress.
When the owner of the vehicle with the transponder in the pocket walks towards the car, the doors of the car will automatically open once the owner is within a few feet from the car. One does not need to search frantically for the remote control of the car in order to open it. Other features incorporated may include the triggering of lights when the doors opened, auto lock once the owner moves away from the car and other features. Many luxury cars manufacturers have already implemented this keyless lock technology in their vehicles and it is forecast that middle range cars will follow suit soon.
Microchip new PIC16F639 flash MCU which has 3 channel, transponder analog front end and KEELOQ cryptographic peripheral is an ideal microchip to be used in the transponder. The 3 channels has omnidirectional 125kHz low frequency communication that are used to communicate with the base station or the reader. This device can also be used in other wireless authentication applications. An example of the passive keyless entry application circuit is shown below.
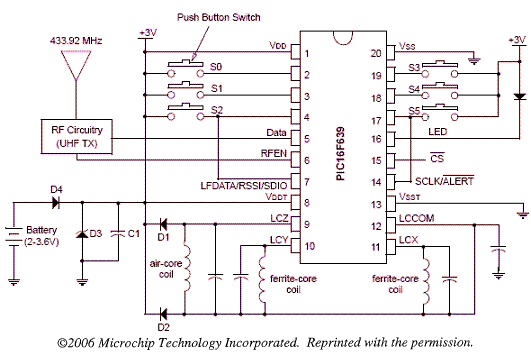
The KEELOQ technology is a non linear encryption algorithm that creates a unique transmission on every use, making the capturing and resending of the same code useless. Hence the security feature is protected from intruders.
This solution from Microchip contains 3 modules. They are the Key Fob, the Base Station and the Receiver/Decoder.
The Base Station starts the communication with the Key Fob by sending out the 125kHz signal. The Key Fob receives and decodes the challenge from the Base Station. If there is a match, the Key Fob will transmit a 432MHz signal back to the Receiver/Decoder. If the Receiver/Decoder recognizes the Key Fob as a valid device, it will send out a signal to unlock the door.
Full detailed application notes with schematic design can be obtained from Microchip Website.

0 comments:
Post a Comment